Website Security Introduction
In today’s digital age, website security is crucial for protecting sensitive data, maintaining user trust, and ensuring uninterrupted service. With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber attacks, a compromised website can lead to significant financial loss, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Ensuring robust security measures not only safeguards your website but also fosters a safe online environment for your users. In this post, we will discuss 7 essential WordPress security tips to keep your organization’s website and its users safe from cyber threats.
WordPress powers over 40% of all websites on the internet, making it the most popular content management system (CMS) globally. Its widespread use, extensive plugin ecosystem, and open-source nature make it an attractive target for cyber attacks. Hackers frequently exploit vulnerabilities in outdated themes, plugins, and the core software to gain unauthorized access, inject malicious code, and disrupt website operations. This popularity, coupled with varied security practices among users, underscores the critical need for robust cyber security measures for WordPress sites.
1. Understanding Cyber Threats
Common Cyber Threats
Malware
Definition: Malicious software designed to infiltrate, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems.
Impact: Can lead to data theft, site defacement, and compromised user information.
Brute Force Attacks
Definition: A method where attackers attempt to gain access by trying multiple username and password combinations until they find the correct one.
Impact: Can result in unauthorized access, data breaches, and administrative control of the site.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Definition: An attack where multiple compromised systems are used to flood a target website with traffic, overwhelming its resources and causing it to become unavailable.
Impact: Can lead to website downtime, loss of revenue, and a negative user experience.
SQL Injection
Definition: An attack that involves inserting malicious SQL code into a query input field to manipulate the database.
Impact: Can result in unauthorized access to the database, data leakage, and corruption of data.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Definition: A vulnerability that allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into webpages viewed by other users.
Impact: Can lead to data theft, session hijacking, and spreading of malware.
Phishing
Definition: A technique used to trick users into providing sensitive information by pretending to be a trustworthy entity.
Impact: Can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and unauthorized access to accounts.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
Definition: An attack where the attacker secretly intercepts and possibly alters the communication between two parties.
Impact: Can result in eavesdropping, data theft, and compromised communication integrity.
Ransomware
Definition: A type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data and demands a ransom for the decryption key.
Impact: Can cause significant financial loss, data loss, and operational disruption.
Understanding these threats is the first step in implementing effective security measures to protect your WordPress website.
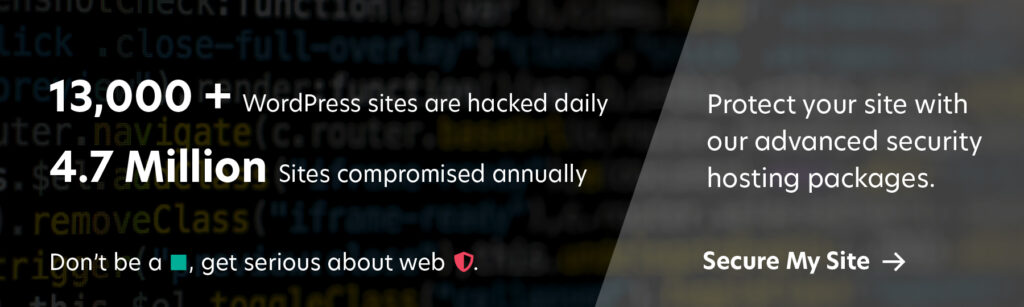
WordPress sites are often targeted by cyber attackers for several reasons:
Popularity and Market Share
WordPress powers over 40% of all websites, making it the most widely used content management system (CMS). Its vast user base makes it an attractive target for hackers, who can potentially exploit vulnerabilities on a large number of sites with a single attack.
Open Source Nature
While being open source allows for community-driven development and transparency, it also means that the codebase is publicly accessible. Hackers can study the code to find and exploit vulnerabilities.
Varied Website Security Practices
Many WordPress site owners are not security experts and may neglect essential security practices. This includes failing to update the core software, themes, and plugins, which can leave known vulnerabilities unpatched.
Extensive Plugin and Theme Ecosystem
WordPress supports a vast array of plugins and themes, many of which are developed by third parties. Some of these plugins and themes may have security flaws or may not be regularly updated, providing potential entry points for attackers.
Ease of Use
WordPress’s user-friendly nature means it is used by a diverse range of people, from large corporations to small businesses and personal bloggers. This wide adoption includes users who may not have advanced technical skills or security knowledge, increasing the likelihood of insecure configurations.
High-Value Targets
Many WordPress sites contain valuable data, including personal information, payment details, and proprietary content. This makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals looking to steal data or demand ransoms.
Automation Tools
Cyber attackers often use automated tools to scan and exploit vulnerabilities in WordPress sites. These tools can easily target a large number of sites quickly, increasing the efficiency and impact of attacks.
Understanding these factors highlights the importance of implementing strong security measures to protect WordPress sites from becoming easy targets for cyber attacks.
2. Basic Website Security Measures
Regular Updates
Outdated WordPress plugins are the biggest culprit of website security breaches. This is closely followed by an outdated WordPress core, and themes installed on your website, making regular updates your most basic first line of defense against common cyber attacks. A quick way to stay on top of updates is to enable automatic updates on the backend of your WordPress website. This comes with potential minor issues, but none as serious as a security breach.
Strong Passwords
Do yourself a favor and set minimum password requirements for all users on your website. It only takes one negligent user to open the door for hackers and malware to your website, specifically brute force attacks, a method where attackers attempt to gain access by trying multiple username and password combinations until they find the correct one.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
In addition to enforcing strong passwords for all users, enforcing two-factor authentication (2FA) for all users on your website is one of the strongest defenses against cyber attacks. There are various ways to implement 2FA ranging from Google and Microsoft authenticators (often a good choice for companies using Google Workspace or Microsoft Azure to manage their employee directories) to WordPress security plugins such as Loginizer for companies who prefer to keep their employee directories disconnected.
Secure Hosting
A secure web hosting service is important to keeping your site secure. Features to look for in your web hosting provider include SSL certificates, regularly scheduled backups, and firewalls.
Essential WordPress Security Plugins
Our favorite WordPress security plugin is MalCare, as it offers robust security features including a malware scanner, malware remover, WordPress firewall, bot protection, an activity log, vulnerability scanner, WordPress backups, and much more.
As we mentioned above, we also use Loginizer for Two-Factor-Authentication (2FA) in addition to our use of the Malcare WordPress Security plugin. These are not the only options, however, as WordPress has an overwhelming number of WordPress security plugins available to its users. Among these are notable plugins such as Wordfence, Sucuri, and iThemes. Just remember, free protection is better than none, but if you have have a larger website with a lot of users, content, and plugins, a paid solution is likely the best option.
3. Regular Backups
We recommend you back your website up daily—and we adhere to this practice for all of the websites hosted on our servers regardless of which tier. A website cyber attack and impact your ability to run your business, and even cause considerable harm to your reputation. The fastest way to bounce back from a security breach is to restore your website to the most recent clean version of the site while your web developers investigate the cause of the breach.
While you can manage your website backups yourself, which may be a viable option for small businesses, we recommend letting your web hosting providers do this for you. Website backups are complex and contain your entire site structure and database, all of which will need to be audited in the event of a cyber attack to ensure that the culprit is removed and the vulnerabilities that lead to the attack are identified and repaired.
Daily backups are sufficient for many websites, but if you update content on your website multiple times each day, you may be interested in a solution that offers hourly backups of your website.
4. Limiting Login Attempts
Limiting login attempts is crucial because it helps prevent brute force attacks, where attackers systematically try numerous username and password combinations to gain unauthorized access. By restricting the number of failed login attempts, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of a successful breach and protect sensitive information on your WordPress site.
You can limit the number of login attempts using different WordPress security plugins, such as Loginizer, as we mentioned before. Loginizer enables login attempt limits to protect your site against brute force attackers, in addition to allowing you to utilize 2FA for added security.
5. Securing the Admin Area
Changing the default login and admin URLs is a great way divert attackers from finding your login prompts altogether. By default, WordPress’ login and admin pages are assigned URL slugs of /wp-login and /wp-admin. This is common knowledge for any attackers crawling the web. By changing these URLs, you will protect your site from common malware attackers as they won’t know the URLs required to log into your site. This is another powerful security feature of the Loginizer WordPress Security plugin.
6. Regular Website Security Audits
Performing regular website security audits gives you team insights to new security vulnerabilities and suspicious activity on your website. You can do this by hiring a professional developer to conduct an audit and interpret the results, or you can use WordPress Security plugins such as MalCare which helps prevent and remove malware in the case of an attack.
How to interpret and act on audit results to improve website security:
Depending on the skill of your team, it is likely in your best interest to hire a professional to interpret and resolve the issues found on your website security audit—especially if your site has been infected with malware. This is due to the fact that even after Malware has been removed, it is likely that it will find its way back into your website through the same vulnerabilities if they are not properly patched.
7. Educating Users About Website Security
Training users on basic website security practices is another strong first step to securing your website. Negligent security practices of users can have detrimental effects on your website’s health. Encouraging awareness of phishing and social engineering attacks, in addition to password strength and best practices will reduce the likelihood of users becoming a security vulnerability.
Bring Your Website Security Full Circle
Securing WordPress websites is essential to protect sensitive data, maintain user trust, and ensure the site’s continuous operation. Given WordPress’s popularity, its sites are frequent targets for cyber attacks. Implementing robust security measures—such as regular updates, strong passwords, limiting login attempts, and using WordPress security plugins—can significantly reduce vulnerabilities and safeguard against common threats like malware, brute force attacks, and DDoS attacks. Ensuring strong security practices is crucial for preventing financial loss, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
Sites of all sizes can be targets of a cyber attack. Whether you are running a large corporation, medium-sized startup, or a small local business, WordPress security best practices should always be followed to keep your business and its online visitors safe. We recommend starting with the basic steps outlined above to keep your site running smoothly, and keep your users and information safe from cyber attacks.
